How Staying Hydrated Can Improve Your Sleep Quality
Sleep is one of the body’s most essential functions, a restorative state necessary for physical healing, mental clarity, and emotional balance. Yet, for many, restful sleep remains elusive. While much focus has been placed on screens, stress, and schedules, one powerful but under-discussed factor can dramatically impact sleep: hydration. That’s right — something as simple as water could be the missing link in your quest for quality sleep.
Whether you’re struggling with nighttime awakenings, restless legs, or groggy mornings, the answer might lie in your hydration habits. And not just how much you drink, but when, what, and how consistently.
Let’s explore the compelling connection between water and rest.

Understanding the Link Between Hydration and Sleep
Hydration isn't just about quenching thirst. It plays a foundational role in nearly every bodily function — from regulating temperature to flushing toxins, and yes, supporting sleep. Studies have shown that dehydration can disturb sleep architecture, especially the deeper, more restorative stages like REM and slow-wave sleep.
When you're dehydrated, your body may struggle to maintain optimal core temperature, leading to restlessness and frequent wake-ups. On the flip side, overhydration could cause nocturia — the need to wake and urinate frequently at night. It's a fine balance.
Why the Body Needs Hydration During Sleep
Sleep is the time when the body repairs tissues, regenerates cells, and resets. All of these processes are water-dependent. Hydration ensures that:
- Electrolytes remain balanced, which supports nerve communication and muscle function.
- Hormonal secretions like melatonin function correctly.
- Organs like the kidneys continue filtering without overexertion.
Common Signs of Nighttime Dehydration
Many people don’t realize their poor sleep is a result of insufficient water intake. Here are some red flags:
- Dry mouth or throat upon waking
- Headaches in the morning
- Leg cramps or muscle spasms at night
- Frequent dreams of water or thirst
These subtle cues could be your body's SOS for hydration.
Sleep Disruption Caused by Dehydration
When your body lacks sufficient fluids, it enters a subtle stress state. This can:
- Increase your heart rate
- Raise cortisol (stress hormone) levels
- Interrupt the body's natural cooling process
These effects compound to result in lighter, fragmented sleep and lower energy the next day.
The Role of Electrolytes in Restorative Sleep
Electrolytes like magnesium, calcium, and potassium are often overlooked heroes of the sleep cycle. They:
- Calm the nervous system
- Regulate muscle contractions (preventing spasms)
- Promote melatonin production
Even slightly low levels, due to poor hydration, can sabotage your ability to fall and stay asleep.
How Water Regulates Body Temperature During Sleep
Sleep is deeply linked to core body temperature. A drop in temperature signals the brain to initiate sleep. Water helps this process through sweating, respiration, and circulation. Dehydration impairs this thermoregulation, potentially causing overheating and night sweats.
Circadian Rhythms and Fluid Balance
Your internal clock, or circadian rhythm, controls sleep timing. But did you know it also regulates hormones like antidiuretic hormone (ADH)? This hormone helps retain fluid overnight. If you're dehydrated, ADH spikes — disrupting your body’s rhythm and potentially leading to grogginess.
Evening Hydration Tips for Better Sleep
Here’s the trick: you want to hydrate enough in the evening to support sleep but not so much that you’re running to the bathroom.
Try this:
- Hydrate consistently throughout the day, not just at night.
- Sip 6–8 oz of water 90 minutes before bed.
- Avoid chugging water right before sleep.
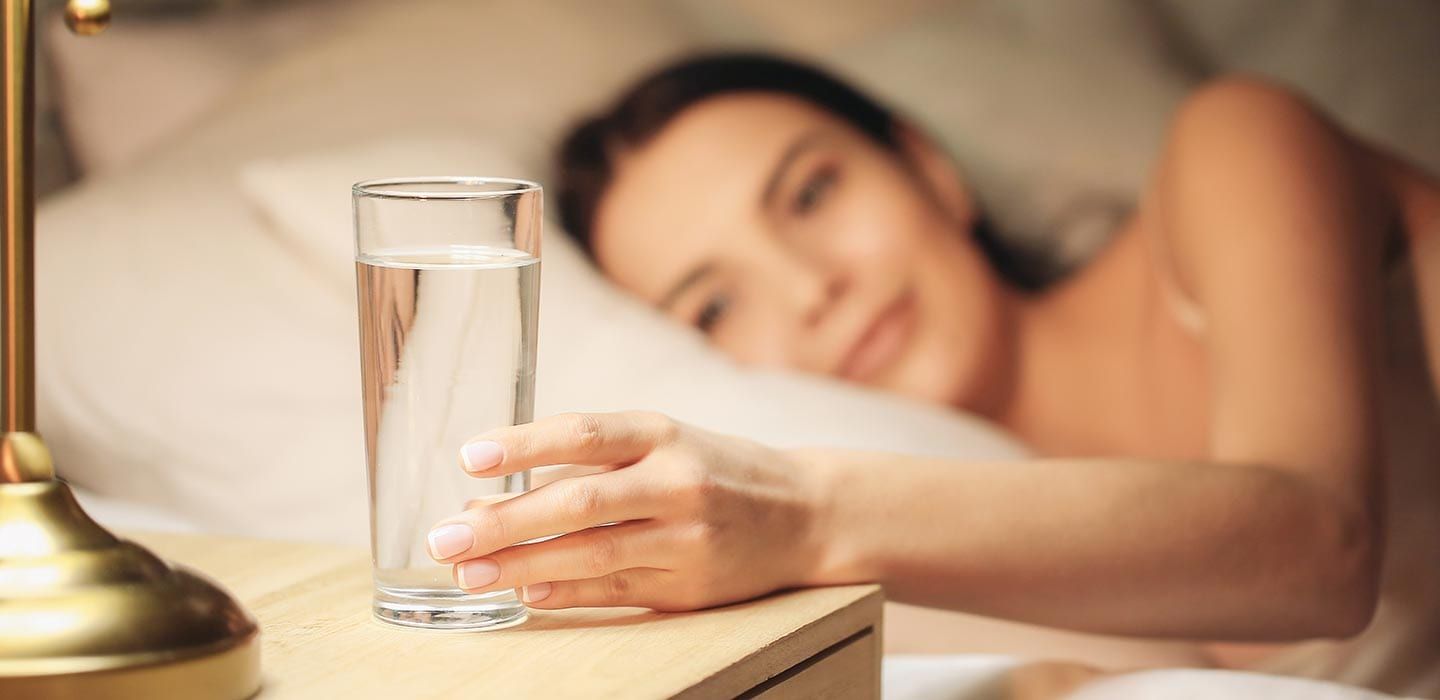
Should You Drink Water Right Before Bed?
Drinking a full glass of water right before sleep might lead to interrupted sleep due to urination. However, a small, electrolyte-rich sip can be beneficial — especially if you sleep in air-conditioned or heated environments.
Best Types of Beverages for Night Hydration
Avoid caffeine and sugar at night. Instead, opt for:
- Chamomile tea (non-diuretic and calming)
- Warm water with lemon
- Coconut water (electrolyte-rich)
- Infused cucumber or mint water
How to Avoid Nocturia from Nighttime Hydration
To avoid middle-of-the-night bathroom trips:
- Limit fluid intake 1 hour before bed
- Elevate your legs for 30 minutes in the evening to reduce fluid pooling
- Use the restroom right before sleep
Effects of Caffeine and Alcohol on Sleep Hydration
Both caffeine and alcohol are diuretics. That means they increase urine output, leading to dehydration. Worse, they disrupt REM sleep. To stay hydrated and sleep well, cut off caffeine by 2 PM and limit alcohol, especially close to bedtime.
Hydration Needs Differ Between Individuals
Your hydration needs vary based on:
- Age: Older adults have reduced thirst signals.
- Gender: Men typically need more water due to higher muscle mass.
- Activity level: Exercise increases water loss via sweat.
How Much Water Do You Really Need Daily for Sleep?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The "8-glass rule" is outdated. Instead:
- Women need ~2.7 liters/day
- Men need ~3.7 liters/day
This includes fluids from food like fruits, soups, and veggies.
Morning Hydration and Its Sleep Impact
Your body loses moisture overnight through breath and sweat. Start the day with 16–20 oz of water to reset hydration and support energy levels. This also helps regulate your body’s sleep-wake rhythm.
Can Overhydration Harm Sleep Quality?
Yes. Drinking excessive water before bed can dilute electrolytes and disturb sleep due to nocturia. Remember: hydration is about consistency, not last-minute water binges.
How Exercise Affects Hydration and Sleep
Exercising in the evening can dehydrate you through sweat. If you don’t replenish those fluids, you risk:
- Leg cramps
- Restlessness
- Higher body temperature
Hydration for Sleep in Different Climates
In dry or high-altitude environments, your body loses more water during the night. A humidifier or extra evening hydration may be helpful. In contrast, tropical climates may require less fluid intake at night.
Seasonal Changes and Sleep Hydration
In winter, heaters dry the air — increasing your hydration needs. In summer, excessive sweating may do the same. Adjust your intake with the seasons.
Sleep Apnea and Hydration
Though not a cure, proper hydration can help keep airways moist, reducing irritation and supporting better oxygen flow — especially in those using CPAP machines.
IV Drip Therapy for Hydration and Sleep Recovery
When regular hydration isn’t cutting it, IV Drip Therapy Service can offer a tailored blend of fluids, electrolytes, and nutrients. It's fast-acting and bypasses the gut, delivering results in minutes. Many clients report better sleep, reduced fatigue, and improved mood after sessions.
Importance of Hydration in Sleep Hygiene
Just like cool rooms and screen-free routines, hydration should be a pillar in your sleep hygiene plan. Set hydration reminders throughout the day to keep your body balanced by bedtime.
Hydration and Mental Health in Sleep
Dehydration can increase cortisol and anxiety — both enemies of sleep. Staying hydrated supports serotonin production and helps reduce insomnia tied to stress.
Dehydration and Sleep in Older Adults
As we age, our body retains less water and our thirst response weakens. Many seniors face sleep challenges due to silent dehydration. Encourage regular sips and hydrating foods.
The Science Behind Hydration-Driven Dreams
Ever notice vivid dreams after a well-hydrated day? Hydration impacts brain activity during REM sleep, possibly influencing dream vividness and memory consolidation.
Sleep Supplements and Hydration Interactions
If you take melatonin, magnesium, or CBD, you’ll want to stay hydrated. These supplements work better when your body’s mineral balance is intact.
Technology and Sleep Hydration
Smart bottles and sleep-tracking apps now monitor both hydration and sleep metrics. These tools can offer insight into how your hydration directly influences your rest.
Hydration Hacks for Better Sleep Quality
- Add chia seeds to your drinks (they retain water)
- Freeze electrolyte popsicles
- Use a bedside water carafe
Daily Routine for Optimal Sleep Hydration
Morning: Drink 16 oz of water
Afternoon: Include hydrating foods
Evening: Sip herbal tea
Night: Stop drinking 90 mins before sleep
Contact a Specialist for Personalized IV Support
If you struggle with chronic dehydration or disrupted sleep, reach out to professionals through this Contact form for guidance tailored to your body’s needs.
FAQs
What happens if I don't drink enough water before bed?
Your body may overheat, muscles might cramp, and you could wake up tired or groggy due to poor sleep cycles.
Is it better to drink cold or warm water before sleeping?
Warm water is better — it relaxes the body and is gentler on digestion.
Can I drink herbal teas instead of water?
Yes, non-caffeinated teas like chamomile or peppermint are hydrating and calming.
What foods help with hydration for sleep?
Water-rich foods like cucumber, watermelon, and lettuce can aid in hydration without overloading your bladder.
How can I tell if dehydration is affecting my sleep?
Signs include waking up tired, having dry eyes or mouth, and frequent muscle spasms.
Do electrolyte drinks help with sleep?
Yes, if they’re low in sugar and caffeine. Look for magnesium or potassium-based ones.
Conclusion
Staying hydrated isn’t just about glowing skin or avoiding fatigue — it’s about reclaiming your rest. Hydration fuels the body’s most vital functions, including the ability to fall asleep and stay asleep deeply. Whether through consistent water intake, smarter beverage choices, or even IV hydration therapy, prioritizing hydration might just be your secret weapon for better sleep.
Links: